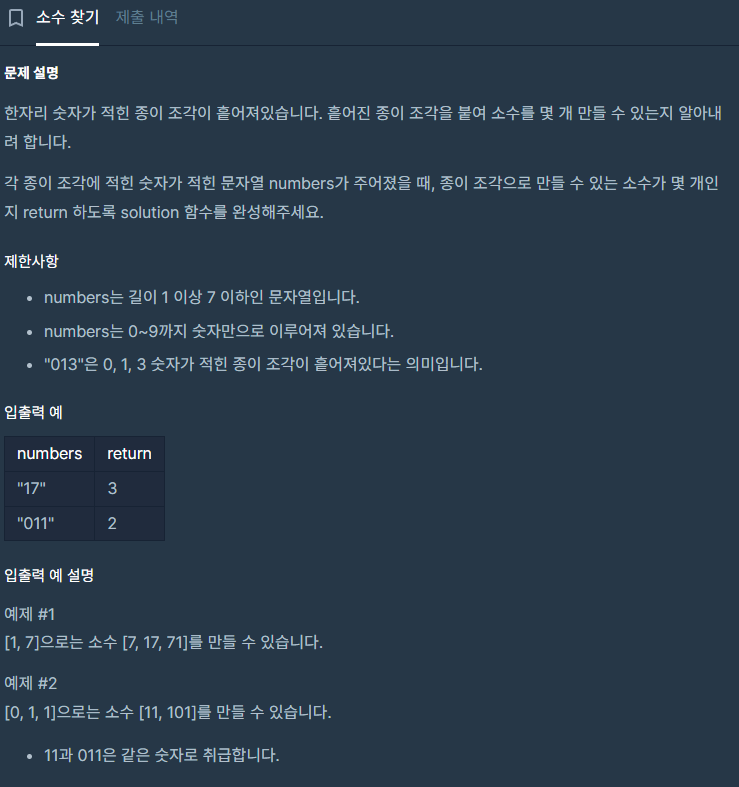
-Code
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
static boolean[] visited;
static Deque<Character> combi;
static Set<Integer> answer = new HashSet<>();
public int solution(String numbers) {
int length = numbers.length();
visited = new boolean[length];
// 길이 1부터 최대 길이까지 탐색
for (int l = 1; l <= length; l++) {
// 길이가 바뀔때마다 초기화
combi = new ArrayDeque<>();
// dfs 시작
DFS(0, numbers, l, length);
}
// 중복없는 소수들의 갯수 반환
return answer.size();
}
// dfs 로직
private static void DFS (int depth, String nums, int targetLength, int totalLength) {
// 현재 길이와 필요 길이가 같고 소수면 저장
if (depth == targetLength) {
int result = isPrime();
if (result != -1) {
answer.add(result);
}
return;
}
// 모든 조합의 수 검사
for (int i = 0; i < totalLength; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
visited[i] = true;
combi.addLast(nums.charAt(i));
DFS(depth + 1, nums, targetLength, totalLength);
combi.pollLast();
visited[i] = false;
}
}
}
// 덱에 있는 문자들을 뽑아서 소수인지 확인
private static int isPrime() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (char ch : combi) {
sb.append(ch);
}
int num = Integer.parseInt(sb.toString());
if (num < 2) return -1;
if (num == 2) return num;
for (int n = 2; n * n <= num; n++) {
if (num % n == 0) {
return -1;
}
}
return num;
}
}처음에 막 짜다 보니 이렇게 복잡하게 짜져서 좀 더 좋은 코드에 대해서나 개선 점에 대해서 찾아봤습니다. 그 결과 빈번한 String 결합과 Integer.parseInt 호출은 메모리 할당(Allocation)을 늘려 성능 저하를 일으킬 수 있다는 것을 알게 되었습니다. 그래서 다른 것들을 참고하여 다음과 같은 코드로 다시 짜봤습니다.
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
static boolean[] visited;
static Set<Integer> answer = new HashSet<>();
public int solution(String numbers) {
visited = new boolean[numbers.length()];
DFS(0, numbers);
return answer.size();
}
// dfs 로직 (depth가 굳이 필요없음)
private static void DFS (int currNum, String nums) {
// 길이에 따른 반환이 없으므로 모든 길이를 돌고
// 모든 길이를 돌면서 소수이면 저장
if (isPrime(currNum)) {
answer.add(currNum);
}
int totalLength = nums.length();
for (int i = 0; i < totalLength; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
visited[i] = true;
// char의 특징을 활용하면 이렇게 될 수 있음
int nextNum = currNum * 10 + (nums.charAt(i) - '0');
DFS(nextNum, nums);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
}
// 소수 확인
private static boolean isPrime(int num) {
if (num < 2) return false;
if (num == 2) return true;
for (int n = 2; n * n <= num; n++) {
if (num % n == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}다시 코드를 참고하며 짜보니까 생각지도 못한 부분도 많고 해서 다음에 비슷한 사례가 나오면 적용할 수 있도록 기억을 잘해둬야겠다고 생각했습니다.
'Beakjoon&프로그래머스 > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준/Java] 20949번 효정과 새 모니터 (0) | 2026.01.06 |
|---|---|
| [백준/Java] 3060번 욕심쟁이 돼지 (0) | 2026.01.06 |
| [프로그래머스/Java] k진수에서 소수 개수 구하기 (0) | 2026.01.05 |
| [백준/Java] 15098번 No Duplicates (0) | 2026.01.05 |
| [백준/Java] 2559번 수열 (1) | 2026.01.05 |